Bats have long been enshrouded in myths and misunderstandings. Often depicted as malevolent creatures in vampire lore and spooky tales, they stir a kind of primordial fear in many people. The image of bats as sinister, bloodthirsty beings couldn't be further from the truth. In reality, these nocturnal mammals are incredibly beneficial to the environment and far from the horror figures popular culture often makes them out to be.
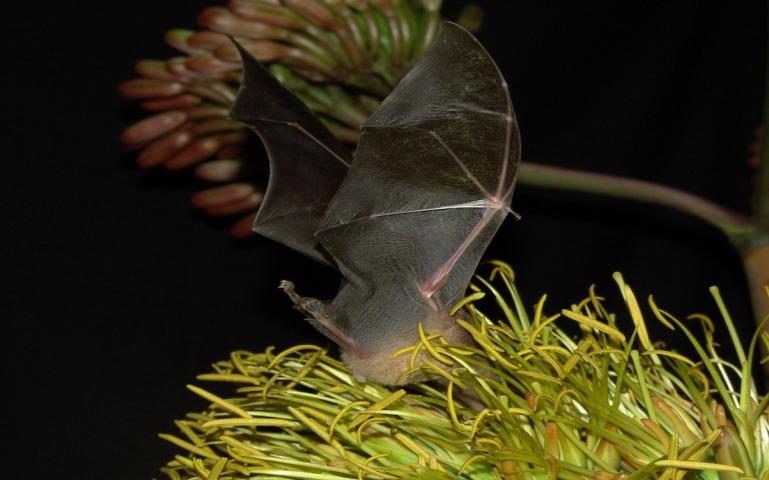

In fact, the more we learn about bats, the more we realize how vital they are to maintaining ecological balance. Let’s delve into the myriad ways these remarkable creatures support the environment and why we should actively work to protect them rather than fear them.
The Ecological Importance of Bats
Bats play critical roles in many environments around the world. As nocturnal animals, they take the night shift to maintain the delicate balance of our ecosystem. Their primary role? Pest control. Bats consume enormous amounts of insects, including mosquitoes and various agricultural pests. This not only makes our summer evenings more pleasant but also benefits farmers by naturally reducing the number of crop-eating insects, which in turn can lessen the need for chemical pesticides.
But the value of bats extends far beyond pest management. They are also key pollinators and seed dispersers. In their nightly forays, nectar-feeding bats pollinate many plants. Remarkably, there are over 300 species of fruit that depend solely on bats for pollination. These include fruits like mangoes, bananas, and guavas, which are staples in the diets of millions of people around the world.
Bats and Tequila: A Unique Relationship
One of the most fascinating aspects of bat pollination is its relationship with the agave plant, the primary ingredient in tequila. Agave plants are adapted to nocturnal pollination and rely on nectar-feeding bats to reproduce. These bats are uniquely suited to pollinate agave because they have evolved to feed on the plant's
nectar, which is only accessible during the night. This nocturnal partnership is crucial; without bats, there would be no natural pollination of agave, and consequently, the production of tequila would be incredibly challenging.
The connection between bats and tequila illustrates the often-unseen impact bats have on our daily lives. Without these flying mammals, not only would the environment suffer, but so would various industries, economies, and cultural practices. This is a perfect example to reflect upon next time a bat swoops by—it might just be a distant cousin of the very creature that helped produce your favorite margarita.
Bats: Pollinators, Seed Dispersers, and More
Beyond pollination, fruit-eating bats are excellent seed dispersers. They help to regenerate forests by spreading seeds over vast areas, including difficult-to-reach locations. This is particularly crucial in deforested or degraded areas where bats help to restore plant diversity. Moreover, their guano (bat droppings) is a highly effective fertilizer, rich in nutrients, and plays a significant role in the nutrient cycle of ecosystems.
Understanding Bat Behavior
The misunderstanding that bats are prone to attacking humans likely stems from their erratic flight patterns. However, what seems unpredictable to us is actually a sophisticated navigation system. Bats use echolocation to find their way in the dark, emitting sounds that bounce off objects and return as echoes, allowing them to construct a sonic map of their surroundings. When a bat "swoops" toward someone, it's usually pursuing an insect attracted to that person, not the person themselves.
Rabies is often a concern associated with bats, and while it is true that they can be carriers, it is worth noting that the likelihood of transmission to humans is extremely low. In fact, you're more likely to come into contact with rabies from a stray dog than a bat. It is always wise to avoid direct contact with any wild animals, but there is no need to fear bats any more than other wildlife.
Bat Conservation: Why It Matters
Bat populations are in decline globally due to habitat loss, climate change, disease (like the White-Nose Syndrome), and direct persecution. This is alarming, considering their ecological and economic importance. By protecting bats, we safeguard our biodiversity and continue to benefit from the services they provide.
Conservation efforts include creating bat-friendly structures, protecting roosting sites, and educating the public about the benefits of bats. Everyone can participate in bat conservation by installing bat houses, preserving natural habitats, and participating in citizen science projects that track bat populations.
Embracing the Night's Winged Protectors
Next time you see a bat flitting about in the evening sky, remember its critical role in our environment. Far from the blood-sucking monsters of myth, bats are protectors of our ecosystems. They ensure the survival of many plant species, keep insect populations in check, and even contribute to the creation of beloved beverages like tequila.
Understanding and appreciating these creatures for what they are—essential players in the circle of life—is the first step toward coexisting with them. By dispelling the myths and embracing the truths about bats, we can work towards a future where these fascinating creatures continue to thrive and benefit the natural world for generations to come.
In conclusion, whether pollinating plants by moonlight, controlling pests under the stars, or simply gracing the twilight with their silent, winged presence, bats are undeniably important. It's time we recognize their value, protect their habitats, and appreciate the myriad ways they contribute to the health of our planet. After all, a world without bats would be a much poorer place indeed.